Welcome To My Blog!
Uniqueness of this Beautiful Island
Let’s Discover Trinidad and Tobago and uncover the wonders of this twin-island country with this comprehensive guide.
Trinidad, the larger of the two islands comprising the nation of Trinidad and Tobago, boasts a rich tapestry of history, politics, and natural wonders. Situated in the southern Caribbean, Trinidad’s geography encompasses diverse ecosystems, from coastal mangroves to lush rainforests. Its biodiversity is a testament to its proximity to South America, with unique flora and fauna found nowhere else in the Caribbean.
Politically, Trinidad operates under a two-party system, with a bicameral parliamentary structure based on the Westminster model. The nation’s history is shaped by colonial influences, including Spanish, British, French, and Dutch rule, leaving behind a legacy of cultural diversity that permeates every aspect of Trinidadian life.
Join us as we delve into the fascinating world of Trinidad, from its history and political landscape, and geography, to its stunning natural beauty and vibrant biodiversity. Plus I’ll throw in some interesting facts that may surprise you!
And, stay tuned for Part 2, where we’ll take a deep dive into Trinidad’s Economic Landscape, Demographics, Language, Education, and Cultural Diversity, along with its Education System, Culture, Sports, and National Symbols.
Discover Trinidad and Tobago: Some Interesting Facts
A twin-island state located off the Venezuelan coast, Trinidad and Tobago is a high-income country with an economy driven by natural gas and petrochemical exports, along with well-developed industrial and financial sectors. With a population of around 1.5 million inhabitants, the nation stands as one of the wealthiest in the Caribbean.
Trinidad and Tobago’s economic prowess stems from its abundant reserves of oil and gas, which serve as the backbone of its economy. This twin-island state, inhabited mostly by people of African and Indian descent, boasts a per capita income exceeding the regional average for Latin America. It is noteworthy that natural gas is poised to surpass oil as the country’s primary source of revenue, with a significant portion exported to the United States.
Other Key Facts:
- Official Name: Republic of Trinidad and Tobago
- Population: Approximately 1.3 million (UN, 2010)
- Capital: Port of Spain
Area: 5,128 square kilometers (1,980 square miles) - Official Language: English
- Major Religions: Christianity, Hinduism, Islam
- Life Expectancy: 74.03 (2023). 71 years for men, 78.2 years for women (UN)
- Monetary Unit: Trinidad and Tobago dollar (1 TTD = 100 cents)
- Main Exports: Petroleum and petroleum products, natural gas, chemicals
Gross National Income (GNI) Per Capita: US $16,330 (World Bank, 2022) - Internet Domain: .tt
- International Dialing Code: +1868
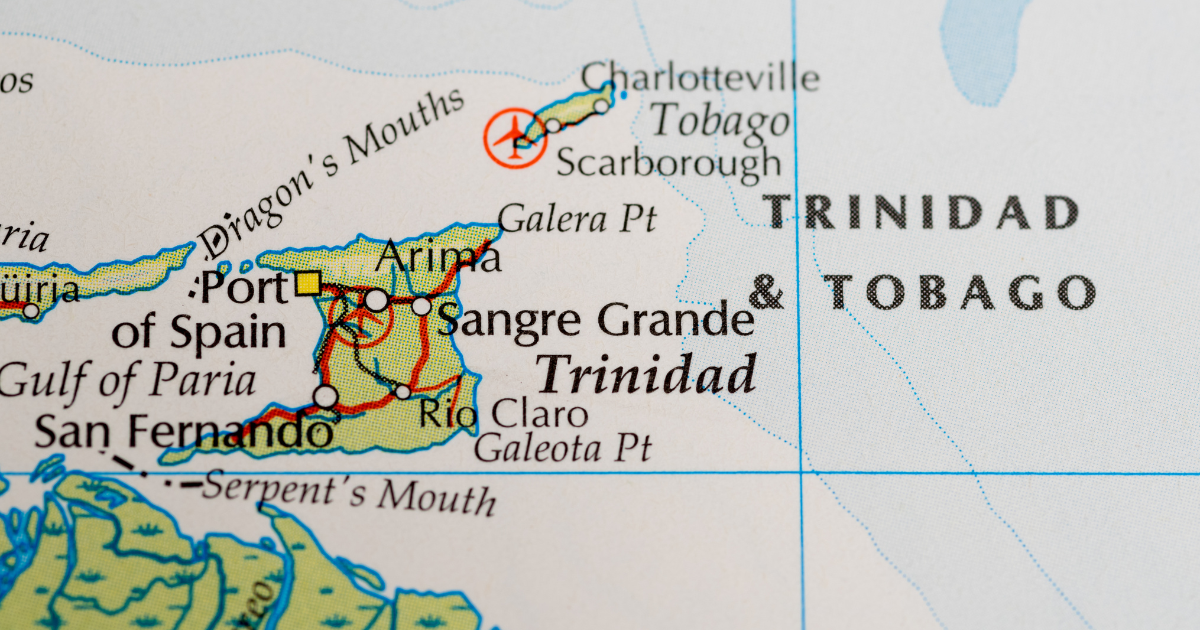
Trinidad and Tobago, officially known as the Republic of Trinidad and Tobago, comprises an archipelagic state located in the southern Caribbean. Positioned just off the northeastern coast of Venezuela and south of Grenada in the Lesser Antilles, it shares maritime boundaries with neighboring nations including Barbados, Guyana, and Venezuela.
The country’s territory spans 5,128 square kilometers (1,980 square miles) and encompasses two main islands, Trinidad and Tobago, along with several smaller landforms. Trinidad, the larger and more populous of the two islands, covers approximately 94% of the total area and hosts 96% of the nation’s population. Notably, Trinidad and Tobago lies outside the hurricane belt, mitigating the risks associated with tropical storms.
Historically, Trinidad was a Spanish colony following the arrival of Christopher Columbus in 1498 until it was ceded to Britain in 1802 under the Treaty of Amiens. Tobago, on the other hand, saw a succession of colonial powers including the Spanish, British, French, Dutch, and Courlanders before also becoming a British possession. The nation gained independence in 1962 and became a republic in 1976.
Unlike many of its English-speaking Caribbean counterparts, Trinidad and Tobago’s economy is predominantly industrial, with a focus on petroleum and petrochemicals. The nation is renowned for its vibrant Carnival celebrations and holds the distinction of being the birthplace of cultural phenomena such as steelpan, calypso, soca, and limbo.
Capital City, Port of Spain
Discover Trinidad and Tobago: A History of Colonial Influence
Trinidad and Tobago, with its rich tapestry of cultures and vibrant history, bears witness to centuries of colonization, struggle, and resilience.
Originally settled by Amerindians of South American origin, Trinidad was inhabited by pre-agricultural Archaic people over 7,000 years ago, making it the earliest settled part of the Caribbean. Ceramic-using agriculturalists arrived around 250 BC, while the Island Caribs and Galibi occupied Tobago.
European contact with Trinidad began when Christopher Columbus encountered the island in 1498. Subsequently, Spanish soldiers, like Antonio de Sedeño, attempted to conquer Trinidad in the 1530s. However, it wasn’t until the arrival of the British in 1797, led by General Sir Ralph Abercromby, that Trinidad became a British crown colony.
Throughout the 19th century, Trinidad’s population saw significant changes due to immigration, including the arrival of French, Scottish, Irish, German, Italian, and English settlers. The abolition of slavery in 1838 led to the introduction of indentured labor, with thousands of Indians brought to Trinidad to work on sugarcane plantations.
In Tobago, colonization by various European powers, including the Dutch, Courlanders, Spanish, French, and British, shaped its history. The islands were consolidated into the colony of Trinidad and Tobago in 1889.
Trinidad and Tobago gained independence from the United Kingdom in 1962, becoming a republic in 1976. Since then, the country has experienced economic fluctuations, with periods of prosperity driven by oil and gas booms, as well as challenges such as political unrest and diversification efforts in the economy.
Today, Trinidad and Tobago stand as a testament to resilience, cultural diversity, and the enduring spirit of its people, shaping a nation that continues to evolve and thrive in the Caribbean region.
Politics in Trinidad and Tobago: A Democratic Republic
Trinidad and Tobago operates as a republic with a two-party system and a bicameral parliamentary system, following the Westminster model. The country’s political landscape is characterized by a vibrant democratic process and regular elections.
At the helm of the nation is the President, serving as the head of state. The President is elected by an Electoral College comprising the full membership of both houses of Parliament. This individual plays a ceremonial role in the government and is responsible for appointing the Prime Minister.
The head of government is the Prime Minister, elected from the results of a general election held every five years. The Prime Minister leads the executive branch of government and is typically the leader of the political party that secures the most seats in the House of Representatives.
In a unique aspect of Trinidad and Tobago’s political system, the President is mandated to appoint the leader of the party with the majority support in the House of Representatives as the Prime Minister. However, this appointment is subject to the President’s discretion and has occasionally led to deviations from traditional party lines.
Tobago, as a distinct entity within the nation, holds its own elections separate from the general elections. Members elected to serve in the Tobago House of Assembly focus on local governance and represent the interests of Tobagonians.
The Parliament of Trinidad and Tobago consists of two chambers: the Senate and the House of Representatives. The Senate comprises 31 seats, with members appointed by the President. This includes Government Senators appointed on the advice of the Prime Minister, Opposition Senators appointed by the Leader of the Opposition, and Independent Senators representing various sectors of civil society.
On the other hand, the House of Representatives consists of 41 members elected by the people through a “first past the post” system. These elected representatives serve a maximum term of five years and play a crucial role in legislative decision-making and governance.
Trinidad and Tobago’s political structure reflects a commitment to democratic principles, fostering a system of checks and balances to ensure effective governance and representation for all citizens.
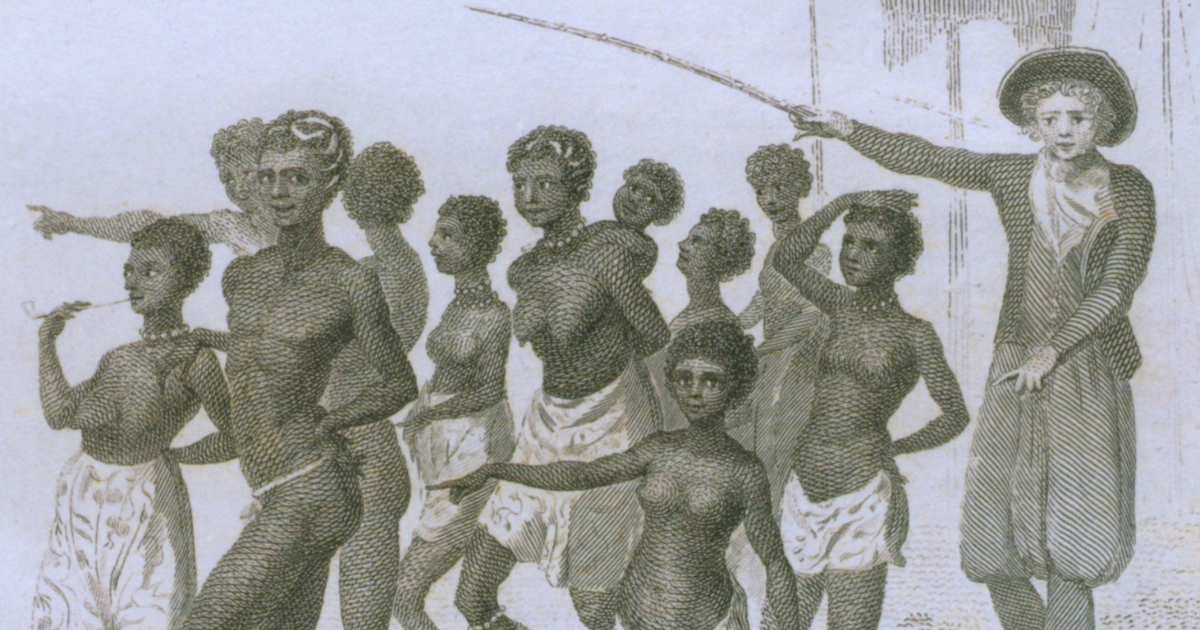

Colonization by various European powers
Biodiversity of Trinidad and Tobago: A Rich Tapestry
Trinidad and Tobago, positioned near continental South America, boast a unique biological diversity that sets them apart from other Caribbean islands, sharing many species with Venezuela. The islands encompass a range of ecosystems, including coastal and marine areas, forests, freshwater bodies, karst formations, and savannas.
In 1996, Trinidad and Tobago ratified the Rio Convention on Biological Diversity, affirming the significance of preserving biodiversity for the well-being of its people. The country has since developed a biodiversity action plan and produced reports outlining its conservation efforts.
The islands host a diverse array of animals, with notable figures including 467 bird species (including one endemic), over 100 mammal species, around 90 reptile species (with one endemic), approximately 30 amphibian species (including one endemic), 50 freshwater fish species, and over 950 marine fish species. Invertebrate data remains incomplete, but highlights include 650 recorded butterfly species, over 672 beetle species (from Tobago alone), and 40 coral species.
Trinidad and Tobago also boast a rich fungal diversity, with 1647 recorded species, including lichens. However, the true number of fungi is likely much higher, with only a fraction of global fungal species currently documented.
Microorganisms contribute to the islands’ biodiversity, with nearly 200 species of marine algae recorded. The full extent of micro-organism species remains unknown but is believed to surpass recorded figures.
Plant diversity is well-documented, with approximately 3,300 recorded species, including 59 endemic species, thanks to recent comprehensive checklists. This rich tapestry of flora and fauna underscores the ecological significance of Trinidad and Tobago in the Caribbean region.
Geography of Trinidad and Tobago: A Diverse Island Nation
Trinidad and Tobago, nestled in the southeastern Caribbean, are situated between 10° 2′ and 11° 12′ N latitude and 60° 30′ and 61° 56′ W longitude. Trinidad lies a mere 11 kilometers (6.8 mi) off the Venezuelan coast, covering an area of 5,128 km2 (1,980 sq mi), while Tobago spans about 300 km2 (120 sq mi).
Comprising two main islands and several smaller landforms, including Chacachacare, Monos, and Little Tobago, Trinidad and Tobago boast a diverse terrain of mountains and plains. The country’s highest point, El Cerro del Aripo, stands at 940 meters (3,080 ft) above sea level in the Northern Range.
Despite its proximity to South America, Trinidad and Tobago are considered part of the Caribbean, sharing linguistic and cultural ties with other English-speaking Caribbean nations. The climate is tropical, with two distinct seasons: a dry season for the first six months of the year and a wet season in the latter half.
Unlike many other Caribbean islands, Trinidad and Tobago have been fortunate to largely evade major devastating hurricanes. The prevailing northeast trade winds help mitigate the impact of tropical storms, contributing to the islands’ relative safety from natural disasters.
Most of the population resides in Trinidad, home to major cities such as Port of Spain, the capital, San Fernando, and Chaguanas. In contrast, Tobago’s main town is Scarborough. The fertile soils of Trinidad support diverse vegetation, including the national flower, the Chaconia (Warszewiczia coccinea).
Geologically, Trinidad and Tobago boast a rich diversity of rock formations, ranging from metamorphic rocks in the Northern Range to sedimentary deposits in the Central and Southern regions. The Southern Lowlands harbor oil and natural gas deposits, contributing to the country’s economic significance in the region.
Despite its location near South America, Trinidad and Tobago’s inclusion in the West Indies reflects its historical and cultural ties to the Caribbean, making it a unique and vibrant destination in the Caribbean Sea.

Mayaro – Trinidad and Tobago
Discover Trinidad and Tobago For Real…
As we wrap up our exploration of Trinidad and Tobago, it’s clear that these islands are more than just sun, sand, and sea. With a history that’s been shaped by colonial powers and a culture that’s as diverse as it is vibrant, there’s something about this place that captures the imagination.
But our journey is far from over. In Part Two, we’ll dive deeper into the heartbeat of Trinidad, exploring its economic landscape, the makeup of its population, and the colorful tapestry of languages, education, and cultural diversity that defines it.
And let’s not forget about the fun stuff – from the pulsating rhythms of its music scene to the thrill of its sports culture and the pride embodied in its national symbols, there’s no shortage of excitement to uncover.
The Fun Train Carnival 2025
But for those already itching to experience Trinidad’s magic firsthand, why not consider joining us for Carnival 2025? It’s an invitation to immerse yourself in the spirit of the islands, to dance to the beat of the soca drums, and lose yourself in a sea of feathers and sequins. Ready to join the celebration? Sign up now and let’s make unforgettable memories together!
Until next time, keep dreaming, keep exploring, and keep embracing the beauty of this remarkable corner of the world. And who knows? Maybe we’ll see you on the streets of Port of Spain for Carnival 2025 – it’s an adventure you won’t want to miss!
Share your thoughts!

You may also like…
Join a growing community of travelers and get juicy tips and insightful guidance to enhance your travel experiences! Receive the latest blogs, updates, and special offers directly to your inbox! Plus, receive a complimentary 15-minute consultation to kickstart your journey!

0 Comments